Organisation Design 101 - Best Practice (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 26 Slides
ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN PPT DESCRIPTION
The objectives of this document are:
• Explain organisation design in relation to the other attributes of an organisation, such as its people and strategy
• Outline the key success factors in designing an organisation structure
• Explain the high level process and supporting tools
Content:
• Objectives
• Attributes of an organisation
• Organisational structure
• Key success factors
• Design process
• Develop strategy
• Design vertical structures
• Design horizontal processes
• Appendix: Organisational Structure Palate
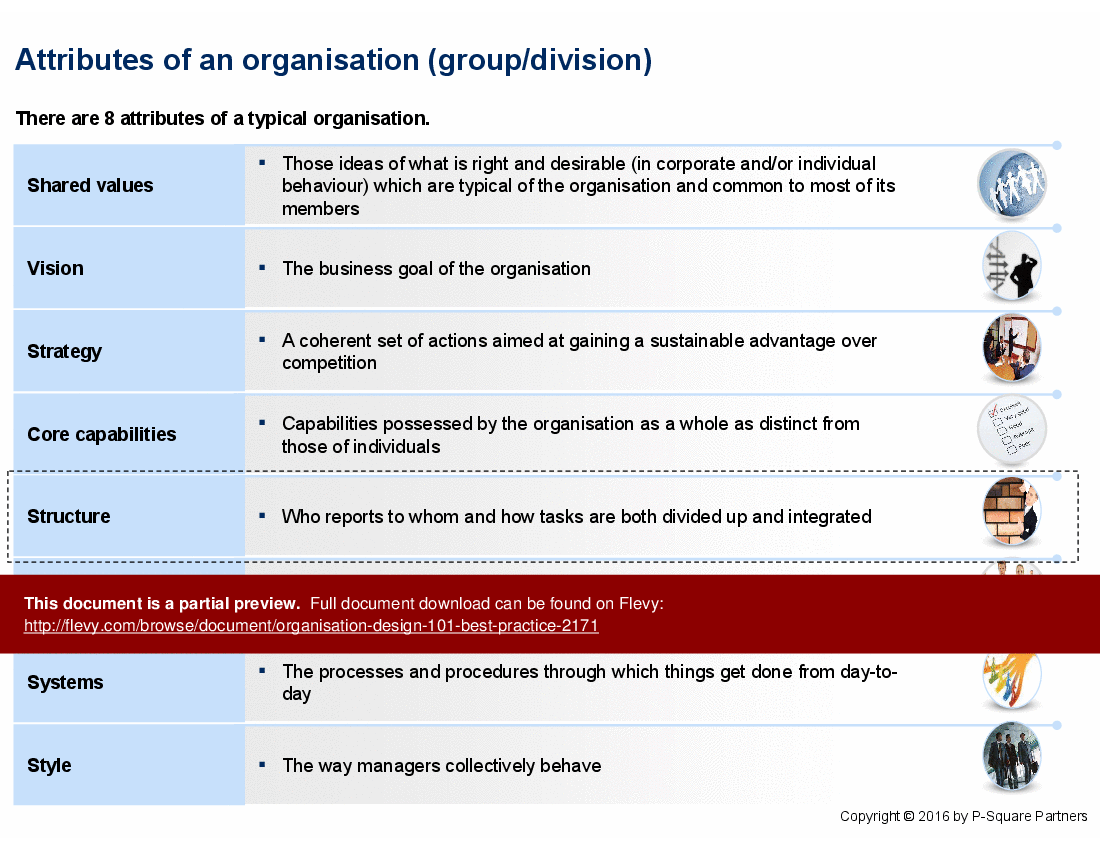
This PPT delves into the eight critical attributes of an organisation, including shared values, vision, strategy, core capabilities, structure, systems, and style. It provides a comprehensive framework for understanding how these elements interplay to create a cohesive organisational design. The insights offered are grounded in practical examples and actionable steps, making it an indispensable resource for executives aiming to optimise their organisational structure.
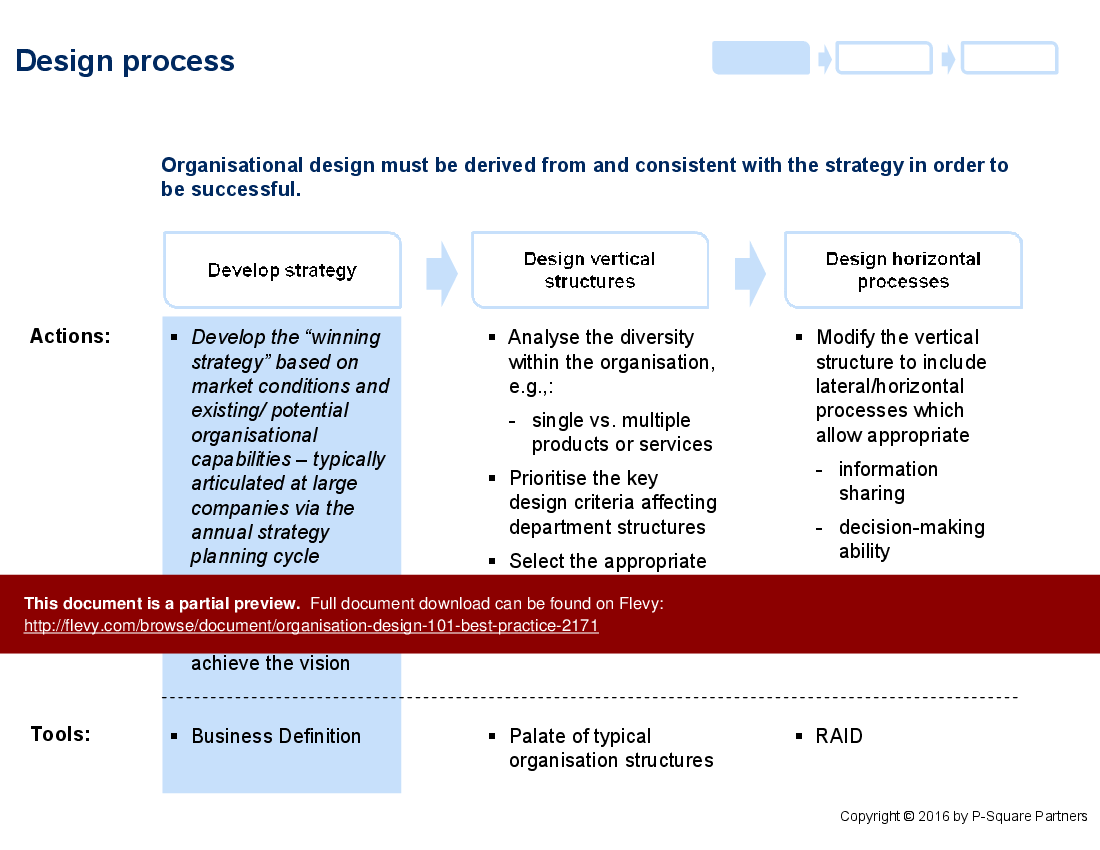
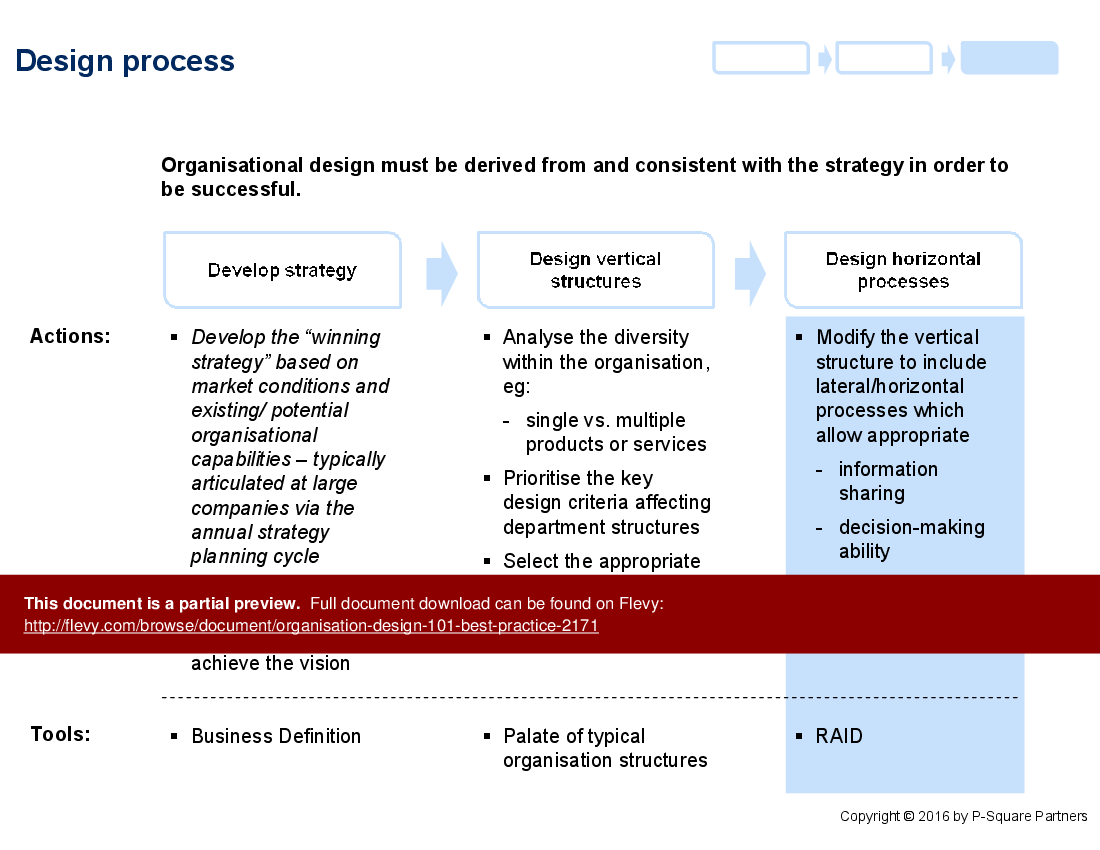
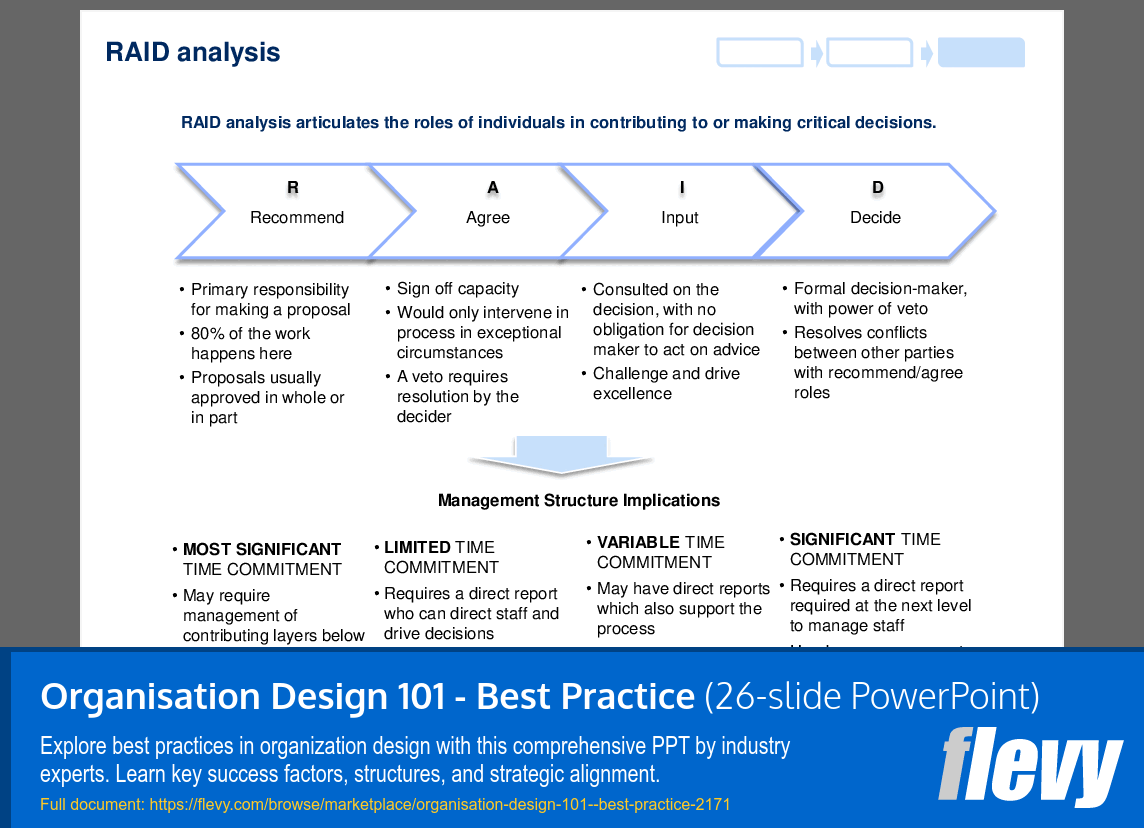
The design process section breaks down the steps necessary to develop a winning strategy, design vertical structures, and implement horizontal processes. This ensures that the organisational design is aligned with the overarching strategy. The document also includes tools like the Business Definition and RAID analysis, which are essential for identifying and developing the necessary horizontal processes within an organisation.
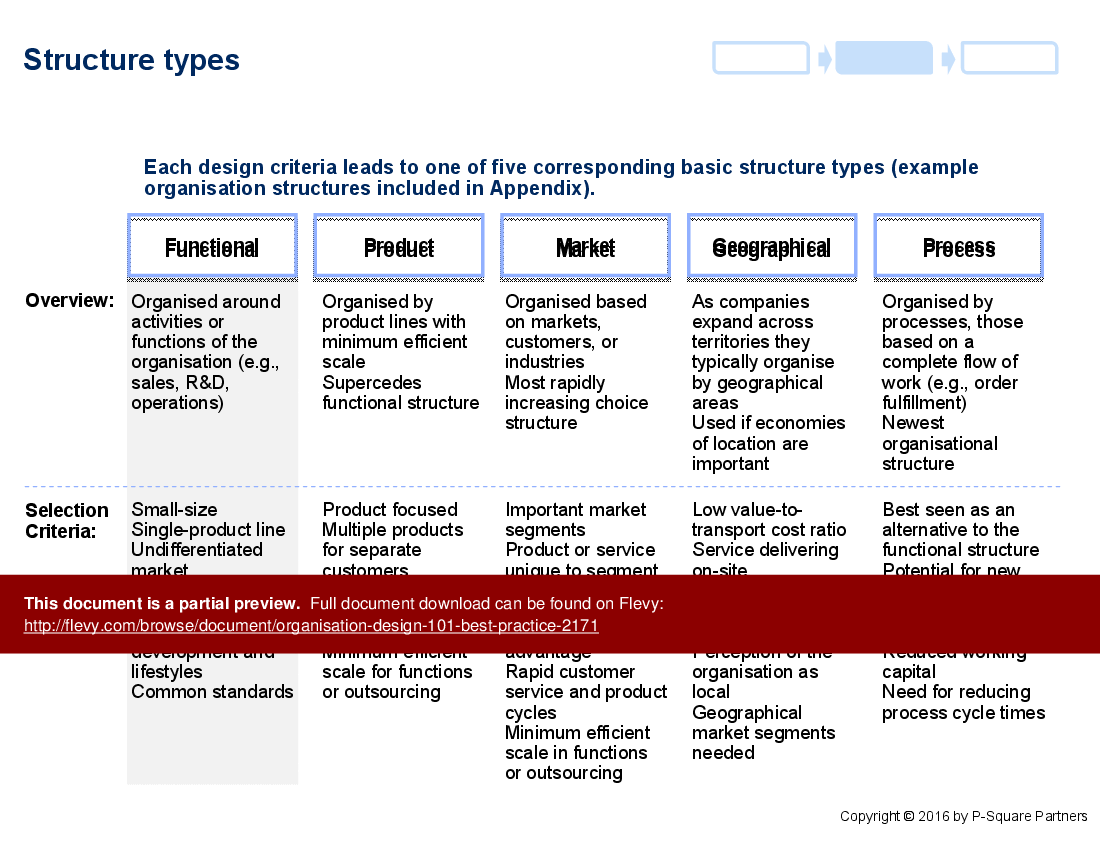
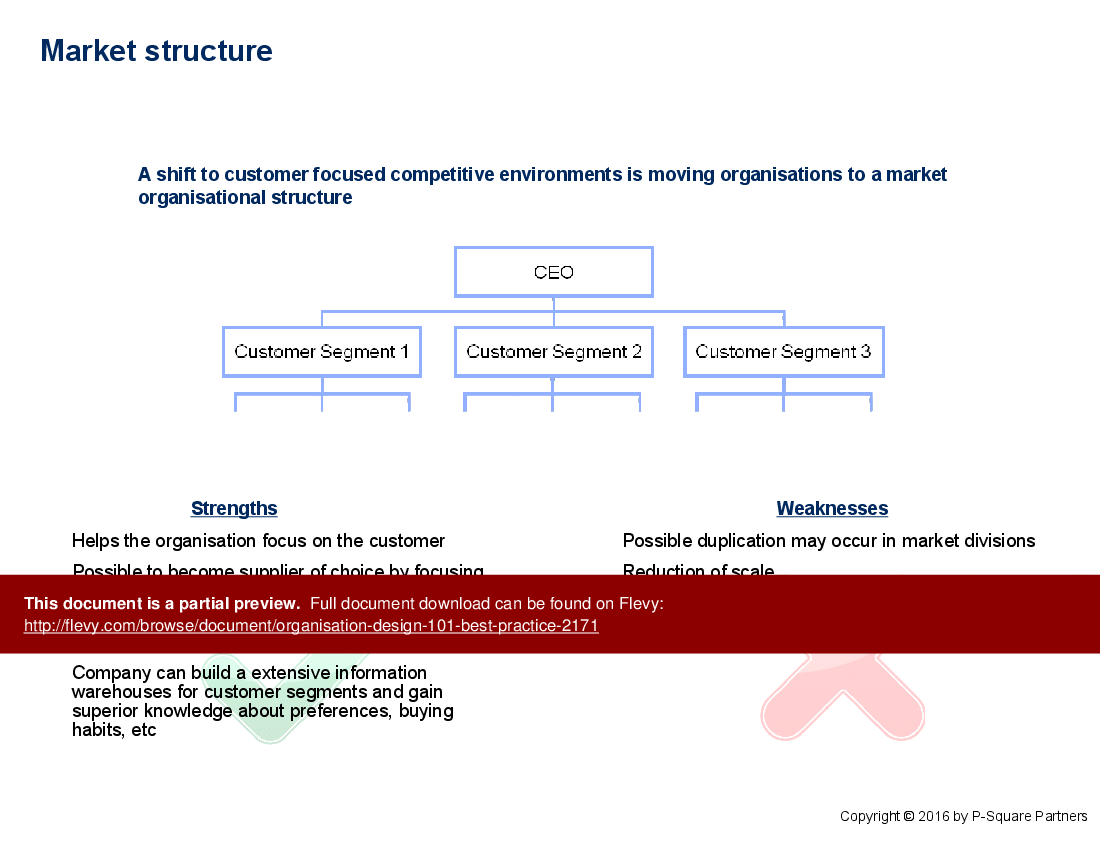
The document also explores various structure types, such as functional, product, market, geographical, and process-based structures. Each type is discussed in terms of its overview and selection criteria, providing a clear understanding of when and how to implement each structure. This level of detail ensures that executives can make informed decisions about the most appropriate organisational structure for their specific needs.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 26-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation, "Organisation Design 101 - Best Practice," delivers insights into effective organization design principles, aligning with the quality standards of McKinsey, Bain, or BCG (consulting-grade; not affiliated). It provides a structured approach for corporate executives and consultants to develop, implement, and optimize organizational structures that align with strategic goals. Users will gain the ability to articulate key success factors, design vertical and horizontal processes, and utilize supporting tools for effective implementation.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives overseeing organizational strategy and design
• Integration leaders managing structural changes within divisions or groups
• Consultants advising on organizational effectiveness and design
• HR leaders focused on aligning people and processes with strategic objectives
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to align organizational structure with business goals
• When initiating a redesign of existing organizational frameworks
• In workshops aimed at enhancing cross-functional collaboration and decision-making processes
Learning Objectives
• Define organization design in relation to people, strategy, and structure
• Build a comprehensive organizational structure that supports strategic objectives
• Establish key success factors for effective organization design
• Analyze business diversity to inform structural decisions
• Design vertical structures that facilitate accountability and decision-making
• Implement horizontal processes that enhance flexibility and responsiveness
Table of Contents
• Objectives (page 3)
• Attributes of an Organisation (page 4)
• Organisational Structure (page 5)
• Key Success Factors (page 6)
• Design Process (page 7)
• Develop Strategy (page 8)
• Design Vertical Structures (page 9)
• Design Horizontal Processes (page 10)
• Appendix: Organisational Structure Palate (page 11)
Primary Topics Covered
• Objectives - This section outlines the goals of the presentation, focusing on organization design and its relationship with other organizational attributes.
• Attributes of an Organisation - Discusses shared values, vision, strategy, structure, people, systems, and style as foundational elements of an organization.
• Organisational Structure - Explains how an organization’s structure aligns its attributes to execute strategy and achieve vision.
• Key Success Factors - Identifies critical elements for successful organization design, emphasizing alignment with strategy.
• Design Process - Details the steps for developing a strategy and designing both vertical and horizontal structures.
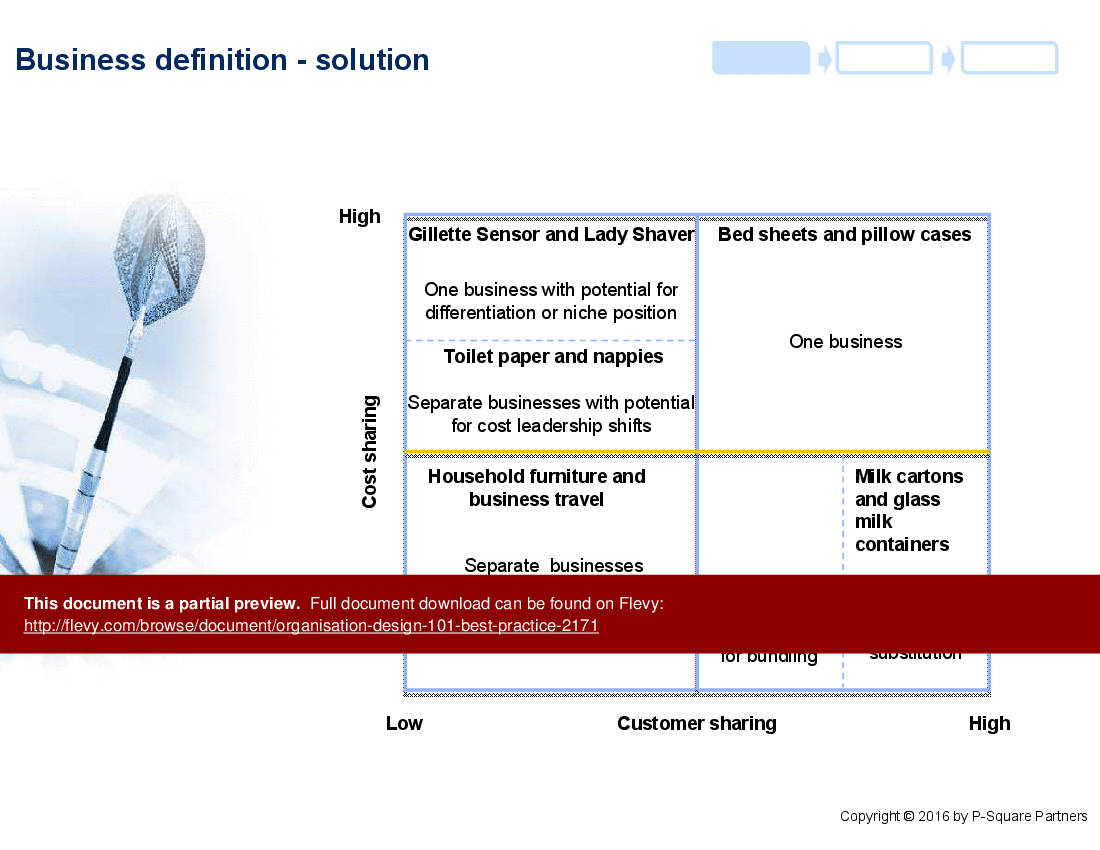
• Business Definition - Explores how to assess business diversity and define the appropriate organizational structure.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Business Definition template for assessing organizational capabilities
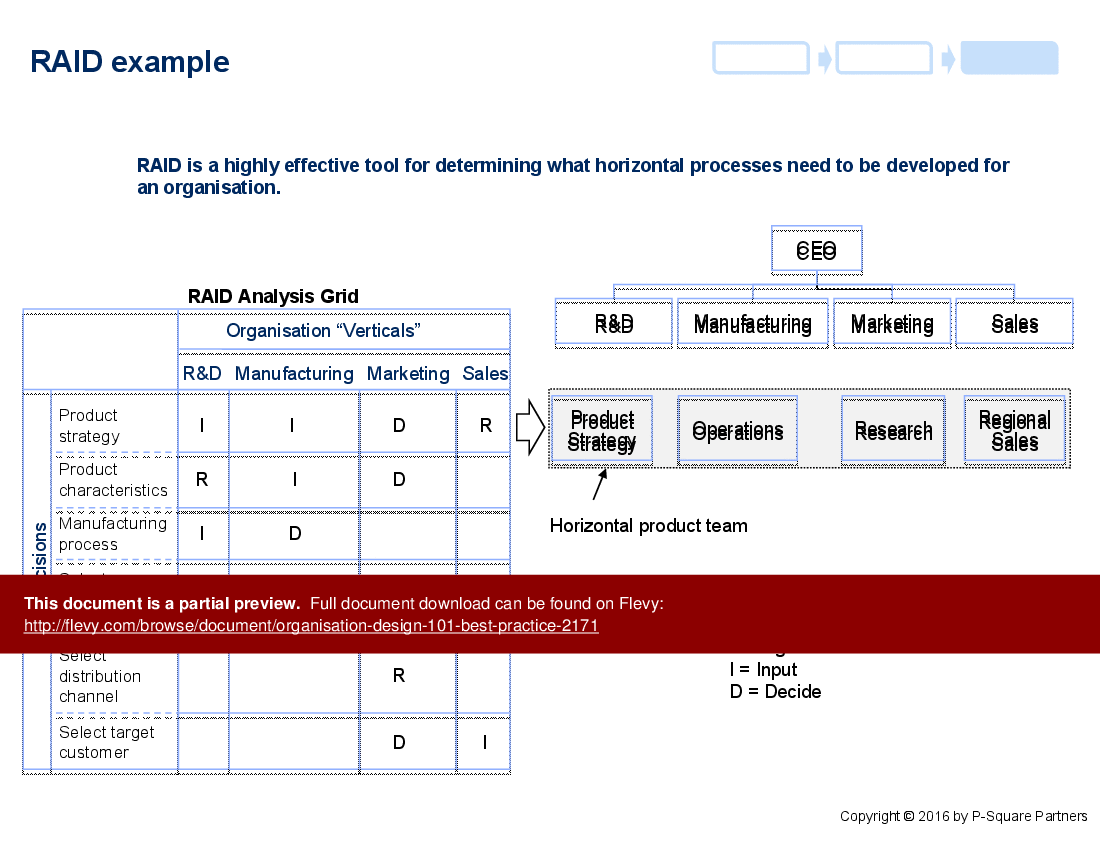
• RAID analysis framework for decision-making roles and responsibilities
• Organizational structure palate for visualizing different structural types
• Vertical structure design criteria checklist for prioritizing design elements
• Horizontal process mapping tools for enhancing cross-functional collaboration
• Implementation roadmap for tracking design changes and outcomes
Slide Highlights
• Overview of organizational attributes and their interconnections
• Key success factors for effective organization design
• Business diversity analysis matrix for determining structural needs
• RAID analysis grid illustrating decision-making roles
• Organizational structure palate showcasing various design types
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Organization Design (30 minutes)
• Overview of objectives and key concepts
• Discussion on the importance of aligning design with strategy
Vertical and Horizontal Structures (60 minutes)
• Breakout sessions to design vertical structures
• Group discussions on horizontal processes and their implementation
Key Success Factors and Tools (45 minutes)
• Presentation on critical success factors
• Hands-on activity using RAID analysis and business definition templates
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the organizational structure palate to reflect specific client needs and contexts
• Adjust the RAID analysis framework to align with existing decision-making processes
• Modify design criteria based on the unique attributes of the organization
Secondary Topics Covered
• The relationship between organizational culture and design
• Strategies for effective communication during redesign processes
• The impact of technology on organizational structure
• Best practices for managing change during implementation
Topic FAQ
What are the core elements of organisation design and how do they interact?
Organisation design links an organisation’s people, strategy, structure, systems, style, shared values, and core capabilities so the structure supports strategic goals and behaviours. The presentation explains how these attributes interconnect to produce coherent design choices and uses visual aids such as the organisational structure palate.How do vertical and horizontal structures differ and when should each be used?
Vertical structures define hierarchy, reporting lines, accountability, and decision-making clarity; horizontal structures define cross-functional processes that improve responsiveness and collaboration. The toolkit guides selection and creation using a vertical structure design criteria checklist and horizontal process mapping tools to choose between them.How should I assess business diversity to choose an organisational structure?
Assess diversity across customer segments, product lines, and markets to decide whether to consolidate or separate functions based on shared customers, costs, and competencies. The deck includes a business diversity analysis matrix and a Business Definition template to support that assessment.What should I look for when buying an organisation design PPT or toolkit?
Look for clear linkage between structure and strategy, practical diagnostic tools (business definition, RAID), visual options for structure types, process-mapping templates, and an implementation roadmap so teams can run workshops and track changes; Flevy’s Organisation Design 101 - Best Practice lists these specific tools and templates.How long should an organisation design workshop run and what agenda items are typical?
A sample workshop agenda in the deck includes a 30-minute introduction to objectives and concepts, 60 minutes on vertical and horizontal structures with breakout sessions, and 45 minutes on key success factors and tool application — a 135-minute sample agenda.After a merger, what steps should I follow to redesign the combined organisation?
Start with a business definition and diversity assessment, define strategy for the combined entity, select structure types with the organisational structure palate, clarify decision rights using RAID analysis, design horizontal processes, and track changes with an implementation roadmap; these steps are outlined in Flevy’s Organisation Design 101 - Best Practice.How can I clarify decision rights and accountability during a redesign?
Use a RAID analysis framework to specify who Recommends, Agrees, provides Input, and Decides for key decisions, document the grid for each process or role, and align reporting lines with those rights; the approach centres on a RAID analysis grid to clarify responsibilities.Are templates and checklists worth the cost compared to building tools from scratch?
Templates consolidate common diagnostics and design steps—business definition, RAID grids, structure palate, process maps, and implementation roadmaps—so teams can apply consistent assessments and run workshops more efficiently; the author describes tools like the Business Definition template as essential for identifying horizontal processes.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is organization design?
Organization design is the process of aligning an organization’s structure with its strategy and objectives to enhance effectiveness and efficiency.
How do I determine the right structure for my organization?
Assess the diversity of your business, including customer segments, product lines, and market needs, to inform the selection of an appropriate organizational structure.
What are the key success factors in organization design?
Key success factors include alignment with strategy, clarity in decision-making processes, and effective communication of design changes.
What tools can assist in the organization design process?
Tools such as RAID analysis, business definition templates, and organizational structure palates can facilitate effective design and implementation.
How can I ensure successful implementation of a new organizational design?
Communicate the reasons for the redesign, provide adequate support and resources, and allow time for the new structure to be fully implemented and tested.
What are vertical and horizontal structures in organization design?
Vertical structures refer to the hierarchy and reporting relationships within an organization, while horizontal structures facilitate cross-functional collaboration and decision-making.
How does business diversity impact organization design?
Understanding business diversity helps determine whether to consolidate or separate functions based on shared customers, costs, and competencies.
What is the RAID analysis framework?
RAID analysis is a tool used to clarify roles and responsibilities in decision-making processes, ensuring accountability and effective collaboration.
Glossary
• Organization Design - The process of structuring an organization to align with its strategy and objectives.
• Vertical Structure - The hierarchy of reporting relationships within an organization.
• Horizontal Processes - Processes that occur across different functions to facilitate collaboration and decision-making.
• RAID Analysis - A framework for defining roles in decision-making processes: Recommend, Agree, Input, Decide.
• Business Diversity - The variety of products, services, and customer segments within an organization.
• Key Success Factors - Critical elements that contribute to the successful design and implementation of organizational structures.
• Organizational Structure Palate - A visual representation of various organizational structures for design reference.
• Decision-Making Processes - Procedures through which decisions are made within an organization.
• Shared Values - The core beliefs and principles that guide an organization’s culture and behavior.
• Strategic Alignment - The process of ensuring that organizational structure and processes support strategic goals.
• Implementation Roadmap - A plan outlining the steps and timelines for implementing organizational design changes.
• Cross-Functional Collaboration - Cooperation between different departments or functions within an organization.
ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Organizational Design PowerPoint Slides: Organisation Design 101 - Best Practice PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, P-Square Partners